An IP stands for internet protocol. An IP address is assigned to each device connected to a network. Each device uses an IP address for communication. It also behaves as an identifier as this address is used to identify the device on a network. It defines the technical format of the packets. Mainly, both the networks, i.e., IP and TCP, are combined together, so together, they are referred to as a TCP/IP. It creates a virtual connection between the source and the destination.
We can also define an IP address as a numeric address assigned to each device on a network. An IP address is assigned to each device so that the device on a network can be identified uniquely. To facilitate the routing of packets, the TCP/IP protocol uses a 32-bit logical address known as IPv4(Internet Protocol version 4).
An IP address consists of two parts, i.e., the first one is a network address, and the other one is a host address.
There are two types of IP addresses:
- IPv4
- IPv6
What is IPv4?
IPv4 is version 4 of IP. It is a current version and the most commonly used IP address. It is a 32-bit address written in four numbers separated by ‘dot’, i.e., periods. This address is unique for each device.
For example, 10.10.1.18
The above example represents the IP address in which each group of numbers separated by periods is called an Octet. Each number in an octet is in the range from 0-to 255. This address can produce 4,294,967,296 possible unique addresses.
In today’s computer network world, computers do not understand the IP addresses in the standard numeric format as the computers understand the numbers in binary form only. The binary number can be either 1 or 0. The IPv4 consists of four sets, and these sets represent the octet. The bits in each octet represent a number.
Each bit in an octet can be either 1 or 0. If the bit the 1, then the number it represents will count, and if the bit is 0, then the number it represents does not count.
Representation of 8 Bit Octet

The above representation shows the structure of 8- the bit octet.
Now, we will see how to obtain the binary representation of the above IP address, i.e., 66.94.29.13
Step 1: First, we find the binary number 66.

To obtain 66, we put 1 under 64 and 2 as the sum of 64, and 2 is equal to 66 (64+2=66), and the remaining bits will be zero, as shown above. Therefore, the binary bit version of 66 is 01000010.
Step 2: Now, we calculate the binary number 94.

To obtain 94, we put 1 under 64, 16, 8, 4, and 2 as the sum of these numbers is equal to 94, and the remaining bits will be zero. Therefore, the binary bit version of 94 is 01011110.
Step 3: The next number is 29.

To obtain 29, we put 1 under 16, 8, 4, and 1 as the sum of these numbers is equal to 29, and the remaining bits will be zero. Therefore, the binary bit version of 29 is 00011101.
Step 4: The last number is 13.

To obtain 13, we put 1 under 8, 4, and 1 as the sum of these numbers is equal to 13, and the remaining bits will be zero. Therefore, the binary bit version of 13 is 00001101.
Drawback of IPv4
Currently, the population of the world is 7.6 billion. Every user is having more than one device connected to the internet, and private companies also rely on the internet. As we know that IPv4 produces 4 billion addresses, which is not enough for each device connected to the internet on a planet. Although the various techniques were invented, such as variable-length mask, network address translation, port address translation, classes, inter-domain translation, to conserve the bandwidth of IP addresses and slow down the depletion of an IP address. In these techniques, public IP is converted into a private IP due to which the user having public IP can also use the internet. But still, this was not so efficient, so it gave rise to the development of the next generation of IP addresses, i.e., IPv6.
What is IPv6?
IPv4 produces 4 billion addresses, and the developers think that these addresses are enough, but they were wrong. IPv6 is the next generation of IP addresses. The main difference between IPv4 and IPv6 is the address size of IP addresses. The IPv4 is a 32-bit address, whereas IPv6 is a 128-bit hexadecimal address. IPv6 provides a large address space, and it contains a simple header as compared to IPv4.
It provides transition strategies that convert IPv4 into IPv6, and these strategies are as follows:
- Dual stacking: It allows us to have both the versions, i.e., IPv4 and IPv6, on the same device.
- Tunneling: In this approach, all the users have IPv6 communicate with an IPv4 network to reach IPv6.
- Network Address Translation: The translation allows the communication between the hosts having a different version of IP.
This hexadecimal address contains both numbers and alphabets. Due to the usage of both the numbers and alphabets, IPv6 is capable of producing over 340 undecillion (3.4*1038) addresses.
IPv6 is a 128-bit hexadecimal address made up of 8 sets of 16 bits each, and these 8 sets are separated by a colon. In IPv6, each hexadecimal character represents 4 bits. So, we need to convert 4 bits to a hexadecimal number at a time
Address format
The address format of IPv4:

The address format of IPv6:
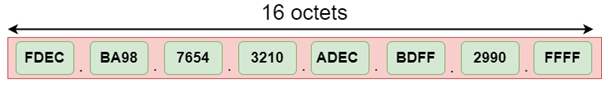
The above diagram shows the address format of IPv4 and IPv6. An IPv4 is a 32-bit decimal address. It contains 4 octets or fields separated by ‘dot’, and each field is 8-bit in size. The number that each field contains should be in the range of 0-255. Whereas an IPv6 is a 128-bit hexadecimal address. It contains 8 fields separated by a colon, and each field is 16-bit in size.
Difference between IPv4 and IPv6
| IPv4 | IPv6 |
|---|---|
| IPv4 has a 32-bit address length | IPv6 has a 128-bit address length |
| It Supports Manual and DHCP address configuration | It supports Auto and renumbering address configuration |
| In IPv4 end to end, connection integrity is Unachievable | In IPv6 end to end, connection integrity is Achievable |
| It can generate 4.29×109 address space | The address space of IPv6 is quite large it can produce a 3.4×1038 address space |
| The Security feature is dependent on the application | IPSEC is an inbuilt security feature in the IPv6 protocol |
| Address representation of IPv4 is in decimal | Address Representation of IPv6 is in hexadecimal |
| Fragmentation performed by Sender and forwarding routers | In IPv6 fragmentation is performed only by the sender |
| In IPv4 Packet flow identification is not available | In IPv6 packet flow identification are Available and uses the flow label field in the header |
| In IPv4 checksum field is available | In IPv6 checksum field is not available |
| It has broadcast Message Transmission Scheme | In IPv6 multicast and anycast message transmission scheme is available |
| In IPv4 Encryption and Authentication facility not provided | In IPv6 Encryption and Authentication are provided |
| IPv4 has a header of 20-60 bytes. | IPv6 has a header of 40 bytes fixed |
