Auditing Standards and Frameworks are guidelines and best practices used by organizations to assess and evaluate their technology infrastructure, processes, and systems. These standards and frameworks provide a comprehensive approach to auditing, covering all aspects of IT infrastructure, including security, performance, compliance, and risk management.
Before going further, let’s understand the common terms:
- Policy: A statement or set of guidelines that outlines an organization’s stance on a specific issue or subject.
- Standard: A set of specifications, requirements, or guidelines that define the expected level of quality or performance for a particular product, service, or process.
- Governance: The process of decision-making and the process by which decisions are implemented, monitored, and reviewed.
- Compliance: Adherence to laws, regulations, standards, policies, and other requirements.
- Control Objective: A desired outcome or result that is achieved through the implementation of specific controls and processes.
- Guideline: A set of recommendations or best practices that provide general direction and guidance on a specific subject or issue.
- Procedure: A detailed, step-by-step description of the process for performing a specific task or achieving a specific objective.
- Baseline: A standard or benchmark that is used as a reference for comparison, measurement, or assessment.
- Regulation: A legally binding rule or requirement that must be followed by organizations and individuals in a specific industry or field.
Auditing Standards and Frameworks
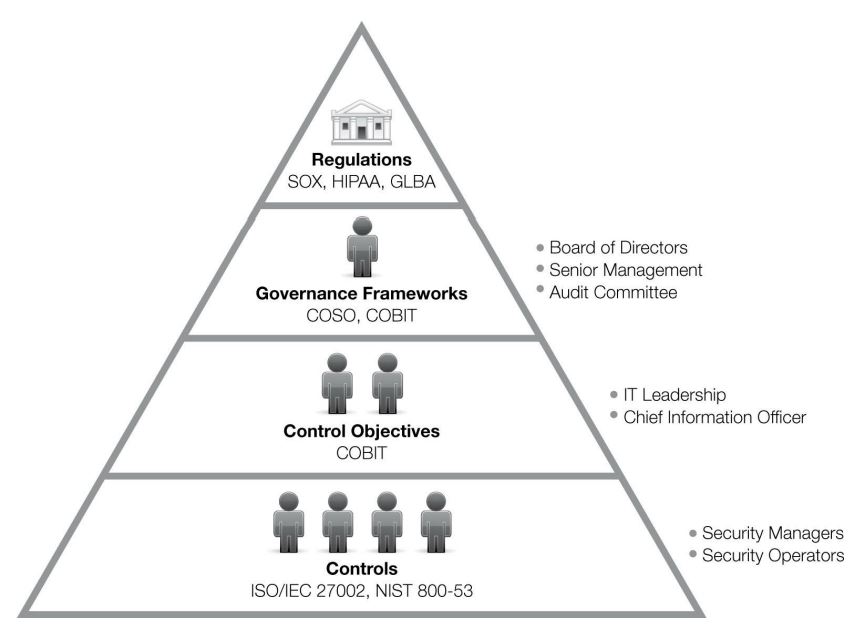
Regulations
Regulation refers to the legal requirements and standards that organizations must comply with when conducting their operations. These regulations may be established by government agencies, industry associations, or other relevant organizations and can cover a wide range of subjects, including financial reporting, data protection, health and safety, and environmental protection.
1. SOX:
The Sarbanes-Oxley Act (SOX) is a US federal law enacted in 2002 in response to the corporate accounting scandals of the late 1990s and early 2000s. The purpose of SOX is to improve the accuracy and reliability of financial reporting by publicly traded companies and to restore public confidence in the financial markets.
SOX requires companies to establish and maintain effective internal controls over financial reporting, and to have their internal controls audited by an independent auditor. The law also imposes various reporting requirements on public companies, including annual reports on the effectiveness of internal controls and certification by the CEO and CFO regarding the accuracy of the company’s financial statements.
SOX also established the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (PCAOB) to oversee the audit of public companies and to enforce compliance with the law. The PCAOB is responsible for setting auditing standards and conducting inspections of public accounting firms to ensure they are following these standards.
2. HIPAA:
The Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) is a US federal law enacted in 1996 to protect the privacy and security of individuals’ personal health information (PHI). The law applies to all entities that handle PHI, including healthcare providers, health plans, and healthcare clearinghouses.
HIPAA sets national standards for protecting PHI and requires organizations to implement administrative, physical, and technical safeguards to secure PHI. The law also requires organizations to provide individuals with access to their PHI, and to give them the opportunity to request that their PHI be amended.
In addition, HIPAA requires healthcare organizations to comply with privacy regulations when disclosing PHI to others, such as healthcare providers, insurance companies, and government agencies. The law also sets penalties for organizations that violate HIPAA’s privacy and security rules, including fines and civil lawsuits.
The purpose of HIPAA is to protect the privacy and security of PHI, to ensure that individuals have access to their PHI, and to promote the proper exchange of PHI between healthcare organizations for the purpose of providing quality healthcare services. HIPAA has been widely credited with improving the privacy and security of PHI, and with helping to ensure that individual’s health information is properly protected and kept confidential.
3. GLBA:
The Gramm-Leach-Bliley Act (GLBA) is a US federal law enacted in 1999 to regulate the financial services industry. The purpose of GLBA is to protect the privacy of consumers’ financial information and to ensure that financial institutions have appropriate security measures in place to protect this information.
GLBA applies to all financial institutions, including banks, credit unions, savings and loans associations, insurance companies, and investment companies. The law requires these institutions to provide consumers with notices about their privacy policies and information-sharing practices and to implement measures to protect consumers’ personal financial information from unauthorized access and disclosure.
In addition, GLBA requires financial institutions to have appropriate security measures in place to protect against unauthorized access to or use of consumer’s personal financial information. This includes implementing administrative, technical, and physical safeguards to protect against unauthorized access and protecting against unauthorized use and disclosure of information.
The purpose of GLBA is to protect consumers’ privacy and ensure that financial institutions have appropriate measures in place to protect personal financial information. GLBA has been widely credited with improving the privacy and security of consumers’ financial information, and with helping to ensure that financial institutions are taking appropriate steps to protect this information.
Governance Framework
A governance framework is a set of rules, policies, and procedures that defines how an organization is managed, how decisions are made, and how the organization is controlled. The framework provides a structure for decision-making and establishes clear lines of authority, responsibility, and accountability within the organization.
1. COSO:
COSO stands for the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission, which is an American organization established in 1985 to promote improvements in corporate governance and financial reporting.
It is best known for its framework for internal control, which provides a comprehensive framework for organizations to assess and improve their internal control systems. The COSO framework includes the following five interrelated components:
- Control environment: The tone of the organization that sets the basis for how controls are implemented.
- Risk assessment: The identification and analysis of risks to the organization’s objectives.
- Control activities: Policies and procedures that help ensure management directives are carried out.
- Information and communication: The flow of information necessary to support the internal control system and make informed business decisions.
- Monitoring: The ongoing assessment of the internal control system to ensure it is functioning effectively.
The COSO framework is widely used by organizations around the world, including those in the private, public, and nonprofit sectors. It is recognized as a best practice for internal control and is often used as a benchmark for evaluating the effectiveness of internal control systems.
2. COBIT:
COBIT (Control Objectives for Information and related Technology) is a framework for the management of information technology (IT) that provides a comprehensive set of guidelines for the governance and management of IT. It was developed by the Information Systems Audit and Control Association (ISACA) to help organizations align their IT strategies with their business objectives.
The COBIT framework includes the following five components:
- Governance: Defines the governance principles and practices for the effective management of IT.
- Management: Provides guidance for the management of IT resources, including the development and maintenance of IT systems and applications.
- Processes: Describes the IT processes necessary for the effective management and control of IT, including planning and organization, acquisition and implementation, delivery and support, and monitoring and evaluation.
- Enabling processes: Provides guidance on the processes required to support the effective management and control of IT, including security and privacy, risk management, and compliance.
- Evaluation: Defines the metrics and measures used to assess the effectiveness of the IT management and control processes.
COBIT is widely used by organizations around the world, including those in the private, public, and nonprofit sectors. It is recognized as a best practice for IT governance and management and is often used as a benchmark for evaluating the effectiveness of IT management systems.
Controls:
Control refers to the process of ensuring that an organization’s objectives and goals are being met through the implementation of specific measures and procedures. The purpose of control in an audit is to mitigate risks, improve the efficiency and effectiveness of operations, and ensure the accuracy of financial reporting.
1. ISO/IEC 27002:
ISO/IEC 27002 is an international standard for information security management that provides guidelines for the implementation of a comprehensive information security management system (ISMS). The standard provides a systematic approach for the management of information security risks, including those related to the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of information.
ISO/IEC 27002 is based on a risk management approach and provides a set of controls that can be implemented to manage information security risks. The standard covers a wide range of topics, including access control, physical security, cryptography, and incident management.
ISO provides a high-level framework that can be customized to meet the specific requirements of an organization. The standard is intended to be used by organizations of all sizes, in all sectors, and in all regions of the world. It is widely recognized as a best practice for information security management and is often used as a benchmark for evaluating the effectiveness of information security management systems.
2. NIST 800-53:
NIST SP 800-53 is a publication from the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) that provides a comprehensive set of security and privacy controls for federal information systems and organizations. This publication is intended to be used by federal agencies to assist in meeting their security and privacy requirements.
NIST SP 800-53 provides a systematic approach for implementing security controls in a manner that is risk-based, flexible, and adaptable to the changing security landscape. The publication is organized into 17 families of security controls that are grouped according to the security functions they address. These control families include access control, awareness and training, incident response, and security management.
The controls provided in NIST SP 800-53 are intended to be flexible and adaptive to the changing security landscape. Organizations are encouraged to use the controls as a baseline, tailoring them to meet their specific needs and requirements. NIST SP 800-53 is widely recognized as a best practice for information security management and is often used as a benchmark for evaluating the security posture of federal information systems and organizations.

Hey this is kinda of off topic but I was wondering
if blogs use WYSIWYG editors or if you have
to manually code with HTML. I’m starting a blog soon but have no
coding know-how so I wanted to get guidance from someone with experience.
Any help would be enormously appreciated!