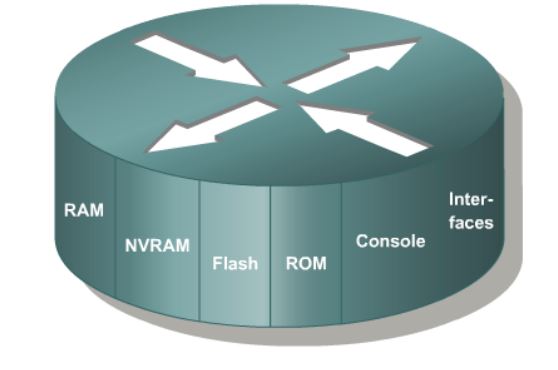
A router is a special type of computer. It has the same basic components as a standard desktop PC. However, routers are designed to perform some very specific functions. Just as computers need operating systems to run software applications, routers need the Internetwork Operating System software (IOS) to run configuration files. These configuration files contain the instructions and parameters that control the flow of traffic in and out of the routers. The many parts of a router are shown below:
Cisco IOS:
Cisco technology is built around the Cisco Internetwork Operating System (IOS), the software that controls internetworking devices’ routing and switching functions. A solid understanding of the IOS is essential for a network administrator.
The Purpose of Cisco IOS:
As with a computer, a router or switch cannot function without an operating system. Cisco calls its operating system the Cisco Internetwork Operating System or Cisco IOS.
Router Memory Components
- ROM
- FLASH Memory
- RAM
- NVRAM
1. ROM:
ROM has the following characteristics and functions:
- Maintains instructions for power-on self-test (POST) diagnostics
- Stores bootstrap program and basic operating system software
- Mini IOS
2. FLASH Memory:
Flash memory has the following characteristics and functions:
- Holds the operating system image (IOS)
- Allows software to be updated without removing and replacing chips on the processor
- Retains content when a router is powered down or restarted
- Can store multiple versions of IOS software
- Is a type of electronically erasable, programmable ROM (EEPROM)
3. RAM:
Random Access Memory is also called dynamic RAM (DRAM). RAM has the following characteristics and functions:
- Stores routing tables
- Holds ARP cache
- Performs packet buffering (shared RAM)
- Provides temporary memory for the configuration file of the router while the router is powered on
- Loses content when the router is powered down or restarted
4. NVRAM:
Non-Volatile RAM (NVRAM) has the following characteristics and functions:
- Provides storage for the startup configuration file
- Retains content when the router is powered down or restarted
- Configuration Register – 16-bit register which decides boot sequence
Interfaces of a Router:
Interfaces have the following characteristics and functions:
Connect the router to the network for frame entry and exit Can be on the motherboard or on a separate module.
Types of interfaces:
- Ethernet
- Fast Ethernet
- Gigabit
- Serial
- Loopback
- Console
- Aux
Router Power-On/Bootup Sequence (0x2102)
- Perform power-on self-test (POST).
- Load and run bootstrap code.
- Find the Cisco IOS software
(A in Flash, B in TFTP Server)- Load the Cisco IOS software.
- Find the configuration.
- (A in NVRAM, B or go in Setup mode)
- Load the configuration.
- Run the configured Cisco IOS software.
Router Power-On/Bootup Sequence (0x2142)
- Perform power-on self-test (POST).
- Load and run bootstrap code.
- Find the Cisco IOS software
(A in Flash, B in TFTP Server)- Load the Cisco IOS software.
- Run the configured Cisco IOS software.
