In our previous post, we discussed the Routing Protocol and Routing Categories and also the types of Routing categories but not in-depth so in this post, we are going to learn in-depth about Routing Categories.
There are mainly three Routing Categories:
- Autonomous System
- EGP
- IGP
Let’s see about it one by one.
1. Autonomous System
An autonomous system (AS) in networking is a collection of one or more associated Internet Protocol (IP) prefixes with a clearly defined routing policy that governs how the AS exchanges routing information with other autonomous systems.
What is an AS routing policy?
An AS routing policy is a list of the IP address space that the AS controls, plus a list of the other ASes to which it connects. This information is necessary for routing packets to the correct networks. ASes announce this information to the Internet using the Border Gateway Protocol (BGP).
- An Autonomous System (AS) is a group of IP networks, which has a single and clearly defined routing policy.
- Group of routers which can exchange updates
- Autonomous systems are identified by numbers
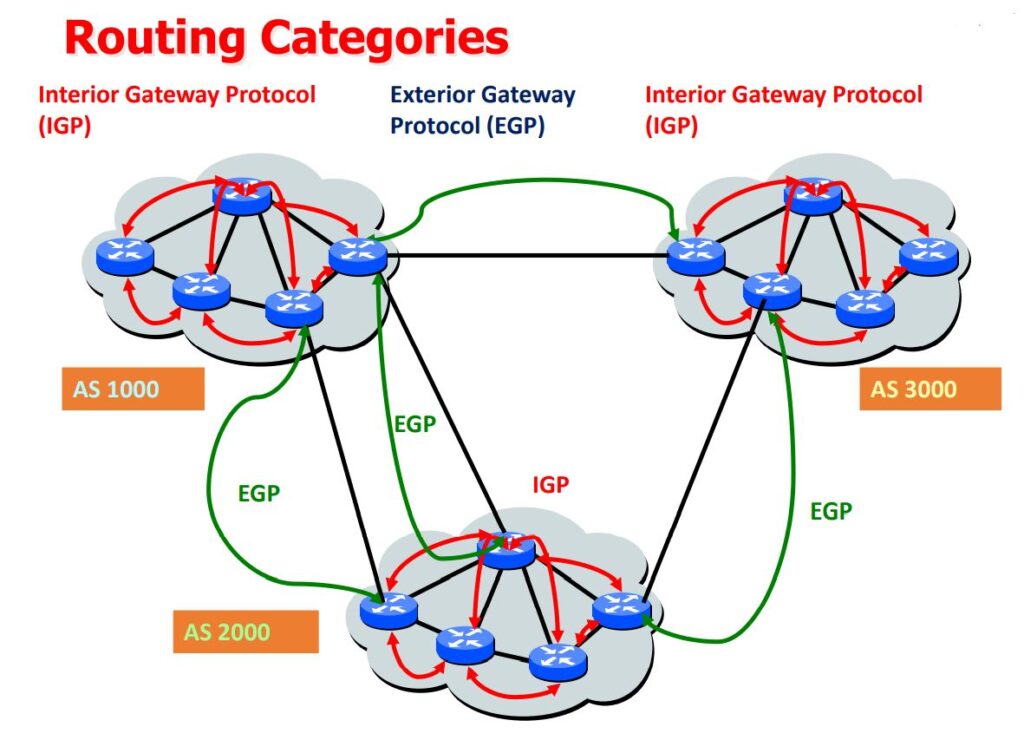
Autonomous Systems: Interior and Exterior Routing Protocols
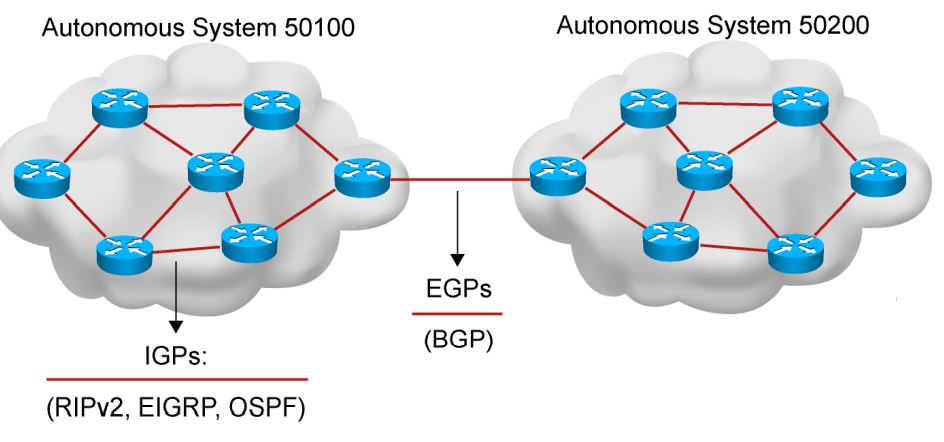
- An autonomous system is a collection of networks within a common administrative domain.
- Interior gateway protocols operate within an autonomous system.
- Exterior gateway protocols connect different autonomous systems.
2. EGP:
Exterior Gateway Protocol (EGP) is a protocol for exchanging routing information between two neighbor gateway hosts (each with its own router) in a network of autonomous systems. EGP is commonly used between hosts on the Internet to exchange routing table information.
- Exterior Gateway Protocols are used for routing between Autonomous Systems
EGP has three major functions:
- Establish a set of neighbors
- Check status of neighbors (if they are alive/reachable)
- Inform neighbors of the networks that are reachable within their AS’s
3. IGP:
IGP, or Interior Gateway Protocol, is a type of routing protocol used for distributing routing information within autonomous systems in large internetworks based on the TCP/IP protocol. A type of routing protocol used for distributing routing information within autonomous systems in large internetworks based on the TCP/IP protocol (such as the Internet).
- Interior Gateway Protocols are used for routing decisions within an Autonomous System.
4. BGP:
ASes announce their routing policy to other ASes and routers via the Border Gateway Protocol (BGP). BGP is the protocol for routing data packets between ASes. Without this routing information, operating the Internet on a large scale would quickly become impractical: data packets would get lost or take too long to reach their destinations.
Each AS uses BGP to announce which IP addresses they are responsible for and which other ASes they connect to. BGP routers take all this information from ASes around the world and put it into databases called routing tables to determine the fastest paths from AS to AS. When packets arrive, BGP routers refer to their routing tables to determine which AS the packet should go to next.
With so many ASes in the world, BGP routers are constantly updating their routing tables. As networks go offline, new networks come online, and ASes expand or contract their IP address space, all of this information has to be announced via BGP so that BGP routers can adjust their routing tables.

Pingback: What is Routing Protocol? Explain its type. - Youngster Company